二叉树(Binary Tree)是指树中节点的度不大于 2 的有序树,它是一种最简单且最重要的树。二叉树的递归定义为:二叉树是一棵空树,或者是一棵由一个根节点和两棵互不相交的,分别称作根的左子树和右子树组成的非空树;左子树和右子树又同样都是二叉树。
二叉树类的基本结构
class TreeNode {
int val;//当前结点值
TreeNode left;//左节点
TreeNode right;//右节点
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}遍历方式
层次遍历
按照二叉树的层次划分进行遍历。
非递归层次遍历
public List<Integer> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//只poll出当前层级的节点进行输出
for (int i = 0, len = queue.size(); i < len; i++) {
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
//将该节点下的下一层级数据加入队列
if (current.left != null) queue.add(current.left);
if (current.right != null) queue.add(current.right);
//保存当前层级的数据内容
result.add(current.val);
}
}
return result;
}前序遍历
前序遍历首先访问根结点然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
举例:
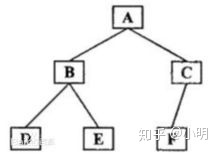
前序遍历结果:ABDECF
注意:已知后序遍历和中序遍历,就能确定前序遍历。
递归前序遍历
public List<Integer> preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) return result;
result.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left, result);
preOrder(root.right, result);
return result;
}迭代前序遍历
public List<Integer> preOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode current = stack.pop();
result.add(current.val);
//将右子节点加入栈中(栈先进后出,先入右再入左,则先取左再取右)
if (current.right != null) stack.push(current.right);
//将左子结点加入栈中
if (current.left != null) stack.push(current.left);
}
return result;
}中序遍历
中序遍历首先遍历左子树,然后访问根结点,最后遍历右子树。
注:二叉搜索树的中序遍历的结果是递增有序的
举例:

中序遍历结果:DBEAFC
注:二叉搜索树题目一般和中序遍历相关。
递归中序遍历
public List<Integer> inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) return result;
inOrder(root.left, result);
result.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, result);
return result;
}迭代中序遍历
public List<Integer> inOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
//遍历到树的最左端,直到current为null
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop();
result.add(current.val);
//current切换到右子树,开始遍历右子树
current = current.right;
}
return result;
}后序遍历
后序遍历首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根结点。
举例:

后序遍历结果:DEBFCA
已知前序遍历和中序遍历,就能确定后序遍历。
递归后序遍历
public List<Integer> postOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) return result;
postOrder(root.left, result);
postOrder(root.right, result);
result.add(root.val);
return result;
}迭代后序遍历
public List<Integer> postOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();//结果集
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
//依次遍历当前结点的左子树
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
TreeNode r = stack.peek();//查看当前栈顶元素
if (r.right == null) {//如果当前栈顶元素没有右子节点
result.add(stack.pop().val);//将其加入结果集
} else {
//否则,先保存当前结点的右子节点并把当前结点的右子节点置为null
// (下次查看当前结点时就会知道右子节点已经遍历过,就可以将其加入结果集了),遍历当前结点右子树
current = r.right;
r.right = null;
}
}
return result;
}