Application Context 是 BeanFactory 的子接口,并提供了更丰富的功能:自动注入、自动配置、生命周期监听等,本文会对 Spring Application Context 的层次及职责进行解析。
ApplicationContext 接口
ACI 继承逻辑
首先需要对 ApplicationContext 聚合的功能进行拆分。以下是 ApplicationContext 的继承结构:
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable,
ListableBeanFactory,
HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource,
ApplicationEventPublisher,
ResourcePatternResolver可以将这些接口大概分为两类:提供配置及资源(EnvironmentCapable、BeanFactory、ResourceLoader)以及提供功能属性(MessageSource、ApplicationEventPublisher)。
EnvironmentCapable
Interface indicating a component that contains and exposes an Environment reference.
public interface EnvironmentCapable {
Environment getEnvironment();
}这与之前在《SpringBoot 启动流程解析》章节中讲到的,在 prepare environment 阶段中配置完成,并在 prepare context 阶段配置到 ApplicationContext 中的 Environment 相同。
ListableBeanFactory 和 HierarchicalBeanFactory
我们先看一下两者与 BeanFactory 的关系,ListableBeanFactory 和 HierarchicalBeanFactory 都继承 BeanFactory。
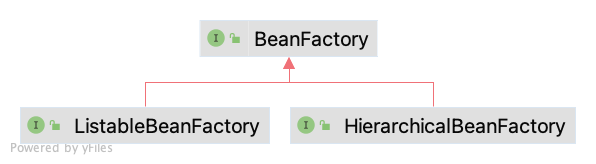
BeanFactory 是访问 Spring Bean Container 的 root 接口,它及它的子接口实现了 Spring 最核心的 Dependency Injection 功能。其有以下功能(只对功能点做一个举例,省略了同名不同参的其他接口):
public interface BeanFactory {
// 获取 Bean Instance
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType);
// 返回一个 Bean Provider,其作用类似于 Optional 的设计模式
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType);
// 返回 Bean name 对应的 Aliases
String[] getAliases(String name);
// 返回 Bean 对应的 Class 类型
Class<?> getType(String name);
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name);
boolean isPrototype(String name);
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch);
}从定义中可以看到,HierarchicalBeanFactory 继承了 BeanFactory,并附加了对 the parent bean factory 访问的权能,即对 BeanFactory 垂直访问的能力。
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
// 与 containsBean 的区别主要是忽略 hierarchy 方向的 Bean
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}同 HierarchicalBeanFactory,ListableBeanFactory 也继承了 BeanFactory,并附加了对 all bean instances 访问的权能,即对 BeanFactory 横向访问的能力。
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
// 与 containsBean 的区别主要是忽略以非 BeanDefinition 注册的 Singleton Bean
// 以及 hierarchy 方向的 Bean
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
// allowEagerInit whether stream-based access may initialize lazy-init
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType, boolean allowEagerInit);
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType);
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> type);
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> type);
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
}MessageSource
MessageSource 用于解析消息,并支持消息的参数化和国际化。 Spring 包含两个内置的 MessageSource 实现:ResourceBundleMessageSource 和 ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource。 后者能够重新加载消息定义,而无需重新启动虚拟机。
public interface MessageSource {
String getMessage(String code, @Nullable Object[] args, @Nullable String defaultMessage, Locale locale);
}ApplicationEventPublisher
ApplicationEventPublisher 封装了事件发布的接口,实现该接口意味着其拥有发布事件的权能。
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
publishEvent((Object) event);
}
void publishEvent(Object event);
}ResourcePatternResolver
ResourcePatternResolver 继承了 ResourceLoader 接口,并被 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 实现。其主要目的是为了加载外部资源进入 Resource,并通过解析被加载入容器。它可以通过 ResourceEditor、ResourceArrayPropertyEditor 实现一些诸如 Listener、Editor 等的扩展功能。
先来看 ResourceLoader,它只提供了根据路径加载 Resource 的方法,以及获取 ClassLoader 的方法。
public interface ResourceLoader {
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}ResourcePatternResolver 继承 ResourceLoader 接口,实现了根据正则表达式批量加载 Resource 的功能。
/**
* <p>{@link PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver} is a standalone implementation
* that is usable outside an {@code ApplicationContext}, also used by
* {@link ResourceArrayPropertyEditor} for populating {@code Resource} array bean
* properties.
*/
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern);
}ACI 派生逻辑
Application 接口派生分为两条线,接口派生以及实现类派生。其主要接口有 WebApplication、ConfigurableApplicationContext、WebServerApplicationContext,由这三个类及其组合接口定义了大体意义上的 Web 服务器功能。
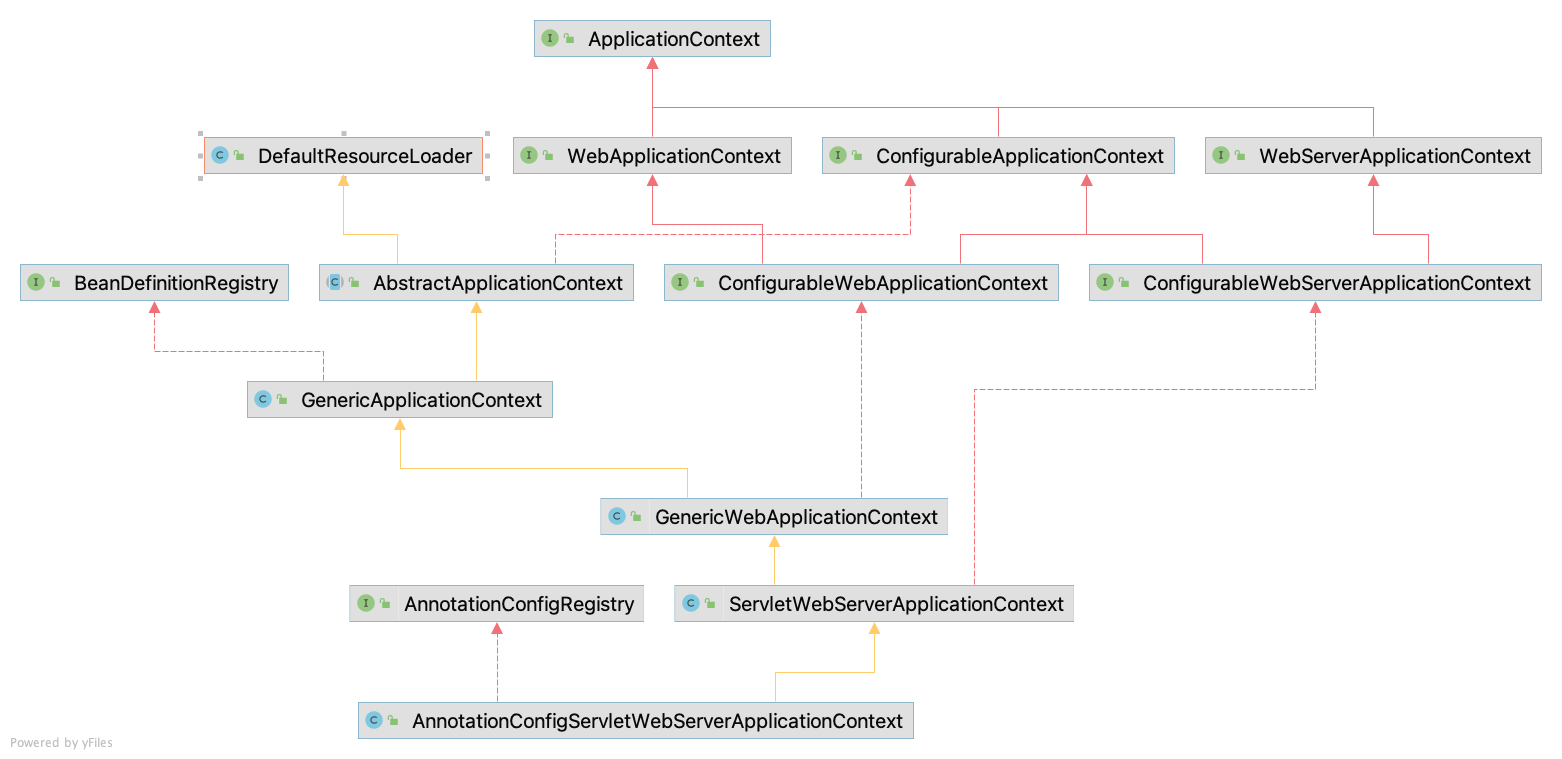
WebApplicationContext 赋予了获取 ServletContext 的权能;WebServerApplicationContext 赋予了获取 WebServer 的权能。ConfigurableApplicationContext 赋予了所需组件的配置权能并定义了 AC 执行流程相关接口。ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 和 ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext 主要是对于 WebApp 和 WebServerApp 进一步的配置。
ApplicationContext 生命周期
在 SpringBoot 启动流程时,将 ApplicationStartup 注入到 ApplicationContext 中,与 SpringApplicationRunListeners 之于 SpringBoot 启动相同,描述了其生命周期阶段。
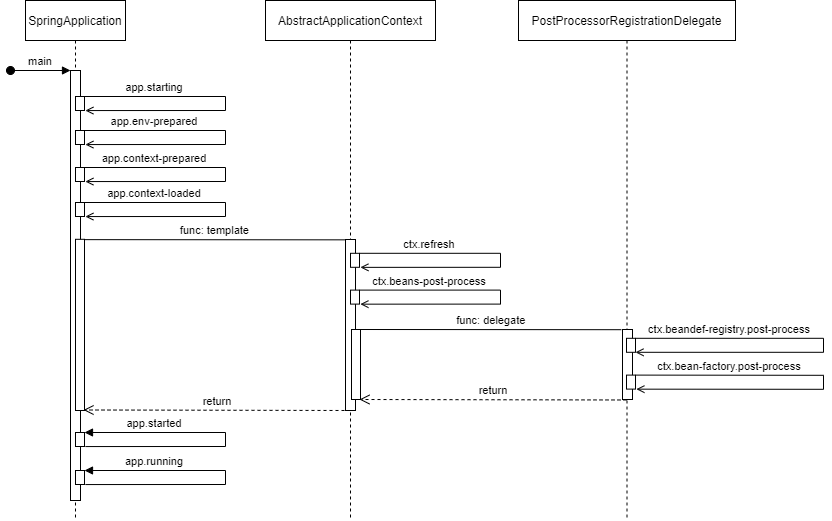
ApplicationContext 实现
AbstractApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext 实现了 ApplicationContext 及 ResourceLoader 接口。具体实现了什么权能在 ApplicationContext 接口部分已经介绍过。
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext
extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext;
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext
extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable;重点关注一下 refresh() 函数,其定义了 ApplicationContext 过程中的重要一步。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 委托 Environment 校验必要配置的内容
// 清理 ApplicationListeners 并初始化 EarlyApplicationListeners
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.\
// 注册以下组件
// 1. BeanFactory ClassLoader
// 2. ResourceEditorRegistrar
// 3. ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 主要处理对 Aware interface 的支持
// 4. 禁止通过 Aware 接口注入相关类
// 5. 允许通过 BeanFactory、ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、ApplicationContext interface 注入
// 6. 提前将 ApplicationListener 注册到 BeanFactory
// 7. 声明 LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor 并准备 weave
// 8. 将环境变量和生命周期回调类注册进 BeanFactory:Environment、SystemProperties、SystemEnvironment、ApplicationStartup
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 模板函数
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// BeanPostProcess StartupStep 过程
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 调用执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 注册 BeanPostProcessor
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 模板方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册 ApplicationListener 和 ApplicationEvent
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 1. 设置 ConversionService
// 2. 设置 EmbeddedValueResolver
// 3. 设置 LoadTimeWeaverAware
// 4. 缓存 all bean definition metadata
// 5. 初始化全部剩余的 non-lazy-init singletons
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}GenericApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext 在继承了 AbstractApplicationContext 的同时实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistry 接口,为其附加了管理 BeanDefinition 的权能。
public class GenericApplicationContext
extends AbstractApplicationContext
implements BeanDefinitionRegistry;具体可以看一下 BeanDefinitionRegistry 定义,详细讲解可以阅读《Spring Bean和BeanFactory层次及职责解析》。
/**
* Interface for registries that hold bean definitions, for example RootBeanDefinition
* and ChildBeanDefinition instances. Typically implemented by BeanFactories that
* internally work with the AbstractBeanDefinition hierarchy.
*
* <p>This is the only interface in Spring's bean factory packages that encapsulates
* <i>registration</i> of bean definitions. The standard BeanFactory interfaces
* only cover access to a <i>fully configured factory instance</i>.
*
* <p>Spring's bean definition readers expect to work on an implementation of this
* interface. Known implementors within the Spring core are DefaultListableBeanFactory
* and GenericApplicationContext.
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry extends AliasRegistry {
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
boolean isBeanNameInUse(String beanName);
}GenericWebApplicationContext
/**
* Subclass of {@link GenericApplicationContext}, suitable for web environments.
*
* <p>Implements {@link org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext},
* but is not intended for declarative setup in {@code web.xml}. Instead, it is designed
* for programmatic setup, for example for building nested contexts or for use within
* {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer WebApplicationInitializers}.
*
* <p><b>If you intend to implement a WebApplicationContext that reads bean definitions
* from configuration files, consider deriving from AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext,
* reading the bean definitions in an implementation of the {@code loadBeanDefinitions}
* method.</b>
*
* <p>Interprets resource paths as servlet context resources, i.e. as paths beneath
* the web application root. Absolute paths, e.g. for files outside the web app root,
* can be accessed via "file:" URLs, as implemented by AbstractApplicationContext.
*
* <p>In addition to the special beans detected by
* {@link org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext},
* this class detects a ThemeSource bean in the context, with the name "themeSource".
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 1.2
*/
public class GenericWebApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {
@Nullable
private ServletContext servletContext;
@Nullable
private ThemeSource themeSource;
/**
* Create a new GenericWebApplicationContext.
* @see #setServletContext
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
* @see #refresh
*/
public GenericWebApplicationContext() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a new GenericWebApplicationContext for the given ServletContext.
* @param servletContext the ServletContext to run in
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
* @see #refresh
*/
public GenericWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Create a new GenericWebApplicationContext with the given DefaultListableBeanFactory.
* @param beanFactory the DefaultListableBeanFactory instance to use for this context
* @see #setServletContext
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
* @see #refresh
*/
public GenericWebApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
}
/**
* Create a new GenericWebApplicationContext with the given DefaultListableBeanFactory.
* @param beanFactory the DefaultListableBeanFactory instance to use for this context
* @param servletContext the ServletContext to run in
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
* @see #refresh
*/
public GenericWebApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(beanFactory);
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Set the ServletContext that this WebApplicationContext runs in.
*/
@Override
public void setServletContext(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return this.servletContext;
}
@Override
public String getApplicationName() {
return (this.servletContext != null ? this.servletContext.getContextPath() : "");
}
/**
* Create and return a new {@link StandardServletEnvironment}.
*/
@Override
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
/**
* Register ServletContextAwareProcessor.
* @see ServletContextAwareProcessor
*/
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
}
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
}
/**
* This implementation supports file paths beneath the root of the ServletContext.
* @see ServletContextResource
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
Assert.state(this.servletContext != null, "No ServletContext available");
return new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, path);
}
/**
* This implementation supports pattern matching in unexpanded WARs too.
* @see ServletContextResourcePatternResolver
*/
@Override
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new ServletContextResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
/**
* Initialize the theme capability.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>Replace {@code Servlet}-related property sources.
*/
@Override
protected void initPropertySources() {
ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Theme getTheme(String themeName) {
Assert.state(this.themeSource != null, "No ThemeSource available");
return this.themeSource.getTheme(themeName);
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Pseudo-implementation of ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public void setServletConfig(@Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
// no-op
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"GenericWebApplicationContext does not support getServletConfig()");
}
@Override
public void setNamespace(@Nullable String namespace) {
// no-op
}
@Override
@Nullable
public String getNamespace() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"GenericWebApplicationContext does not support getNamespace()");
}
@Override
public void setConfigLocation(String configLocation) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"GenericWebApplicationContext does not support setConfigLocation(). " +
"Do you still have an 'contextConfigLocations' init-param set?");
}
}
@Override
public void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations) {
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configLocations)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"GenericWebApplicationContext does not support setConfigLocations(). " +
"Do you still have an 'contextConfigLocations' init-param set?");
}
}
@Override
public String[] getConfigLocations() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"GenericWebApplicationContext does not support getConfigLocations()");
}
}ServletWebServerApplicationContext
/**
* A {@link WebApplicationContext} that can be used to bootstrap itself from a contained
* {@link ServletWebServerFactory} bean.
* <p>
* This context will create, initialize and run an {@link WebServer} by searching for a
* single {@link ServletWebServerFactory} bean within the {@link ApplicationContext}
* itself. The {@link ServletWebServerFactory} is free to use standard Spring concepts
* (such as dependency injection, lifecycle callbacks and property placeholder variables).
* <p>
* In addition, any {@link Servlet} or {@link Filter} beans defined in the context will be
* automatically registered with the web server. In the case of a single Servlet bean, the
* '/' mapping will be used. If multiple Servlet beans are found then the lowercase bean
* name will be used as a mapping prefix. Any Servlet named 'dispatcherServlet' will
* always be mapped to '/'. Filter beans will be mapped to all URLs ('/*').
* <p>
* For more advanced configuration, the context can instead define beans that implement
* the {@link ServletContextInitializer} interface (most often
* {@link ServletRegistrationBean}s and/or {@link FilterRegistrationBean}s). To prevent
* double registration, the use of {@link ServletContextInitializer} beans will disable
* automatic Servlet and Filter bean registration.
* <p>
* Although this context can be used directly, most developers should consider using the
* {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext} or
* {@link XmlServletWebServerApplicationContext} variants.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Scott Frederick
* @since 2.0.0
* @see AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
* @see XmlServletWebServerApplicationContext
* @see ServletWebServerFactory
*/
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext
implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
/**
* Constant value for the DispatcherServlet bean name. A Servlet bean with this name
* is deemed to be the "main" servlet and is automatically given a mapping of "/" by
* default. To change the default behavior you can use a
* {@link ServletRegistrationBean} or a different bean name.
*/
public static final String DISPATCHER_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
private volatile WebServer webServer;
private ServletConfig servletConfig;
private String serverNamespace;
/**
* Create a new {@link ServletWebServerApplicationContext}.
*/
public ServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
}
/**
* Create a new {@link ServletWebServerApplicationContext} with the given
* {@code DefaultListableBeanFactory}.
* @param beanFactory the DefaultListableBeanFactory instance to use for this context
*/
public ServletWebServerApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
}
/**
* Register ServletContextAwareProcessor.
* @see ServletContextAwareProcessor
*/
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
registerWebApplicationScopes();
}
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw ex;
}
}
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
@Override
protected void doClose() {
if (isActive()) {
AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(this, ReadinessState.REFUSING_TRAFFIC);
}
super.doClose();
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
createWebServer.end();
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
/**
* Returns the {@link ServletWebServerFactory} that should be used to create the
* embedded {@link WebServer}. By default this method searches for a suitable bean in
* the context itself.
* @return a {@link ServletWebServerFactory} (never {@code null})
*/
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() {
// Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);
if (beanNames.length == 0) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory bean.");
}
if (beanNames.length > 1) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple "
+ "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames));
}
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class);
}
/**
* Returns the {@link ServletContextInitializer} that will be used to complete the
* setup of this {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* @return the self initializer
* @see #prepareWebApplicationContext(ServletContext)
*/
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return this::selfInitialize;
}
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
private void registerApplicationScope(ServletContext servletContext) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(servletContext);
getBeanFactory().registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
servletContext.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
private void registerWebApplicationScopes() {
ExistingWebApplicationScopes existingScopes = new ExistingWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
existingScopes.restore();
}
/**
* Returns {@link ServletContextInitializer}s that should be used with the embedded
* web server. By default this method will first attempt to find
* {@link ServletContextInitializer}, {@link Servlet}, {@link Filter} and certain
* {@link EventListener} beans.
* @return the servlet initializer beans
*/
protected Collection<ServletContextInitializer> getServletContextInitializerBeans() {
return new ServletContextInitializerBeans(getBeanFactory());
}
/**
* Prepare the {@link WebApplicationContext} with the given fully loaded
* {@link ServletContext}. This method is usually called from
* {@link ServletContextInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)} and is similar to the
* functionality usually provided by a {@link ContextLoaderListener}.
* @param servletContext the operational servlet context
*/
protected void prepareWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
Object rootContext = servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (rootContext != null) {
if (rootContext == this) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - "
+ "check whether you have multiple ServletContextInitializers!");
}
return;
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext");
try {
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name ["
+ WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
setServletContext(servletContext);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - getStartupDate();
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (getServletContext() == null) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
return new ServletContextResource(getServletContext(), path);
}
@Override
public String getServerNamespace() {
return this.serverNamespace;
}
@Override
public void setServerNamespace(String serverNamespace) {
this.serverNamespace = serverNamespace;
}
@Override
public void setServletConfig(ServletConfig servletConfig) {
this.servletConfig = servletConfig;
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return this.servletConfig;
}
/**
* Returns the {@link WebServer} that was created by the context or {@code null} if
* the server has not yet been created.
* @return the embedded web server
*/
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer() {
return this.webServer;
}
/**
* Utility class to store and restore any user defined scopes. This allow scopes to be
* registered in an ApplicationContextInitializer in the same way as they would in a
* classic non-embedded web application context.
*/
public static class ExistingWebApplicationScopes {
private static final Set<String> SCOPES;
static {
Set<String> scopes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST);
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION);
SCOPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(scopes);
}
private final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private final Map<String, Scope> scopes = new HashMap<>();
public ExistingWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
for (String scopeName : SCOPES) {
Scope scope = beanFactory.getRegisteredScope(scopeName);
if (scope != null) {
this.scopes.put(scopeName, scope);
}
}
}
public void restore() {
this.scopes.forEach((key, value) -> {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Restoring user defined scope " + key);
}
this.beanFactory.registerScope(key, value);
});
}
}
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
/**
* {@link ServletWebServerApplicationContext} that accepts annotated classes as input - in
* particular {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration}
* -annotated classes, but also plain {@link Component @Component} classes and JSR-330
* compliant classes using {@code javax.inject} annotations. Allows for registering
* classes one by one (specifying class names as config location) as well as for classpath
* scanning (specifying base packages as config location).
* <p>
* Note: In case of multiple {@code @Configuration} classes, later {@code @Bean}
* definitions will override ones defined in earlier loaded files. This can be leveraged
* to deliberately override certain bean definitions via an extra Configuration class.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.0.0
* @see #register(Class...)
* @see #scan(String...)
* @see ServletWebServerApplicationContext
* @see AnnotationConfigServletWebApplicationContext
*/
public class AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext extends ServletWebServerApplicationContext
implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
private final Set<Class<?>> annotatedClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private String[] basePackages;
/**
* Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext} that needs
* to be populated through {@link #register} calls and then manually
* {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}.
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext} with the
* given {@code DefaultListableBeanFactory}. The context needs to be populated through
* {@link #register} calls and then manually {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}.
* @param beanFactory the DefaultListableBeanFactory instance to use for this context
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext}, deriving
* bean definitions from the given annotated classes and automatically refreshing the
* context.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes, e.g. {@code @Configuration}
* classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
/**
* Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext}, scanning
* for bean definitions in the given packages and automatically refreshing the
* context.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(String... basePackages) {
this();
scan(basePackages);
refresh();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>
* Delegates given environment to underlying {@link AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} and
* {@link ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner} members.
*/
@Override
public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
super.setEnvironment(environment);
this.reader.setEnvironment(environment);
this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment);
}
/**
* Provide a custom {@link BeanNameGenerator} for use with
* {@link AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} and/or
* {@link ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner}, if any.
* <p>
* Default is
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationBeanNameGenerator}.
* <p>
* Any call to this method must occur prior to calls to {@link #register(Class...)}
* and/or {@link #scan(String...)}.
* @param beanNameGenerator the bean name generator
* @see AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#setBeanNameGenerator
* @see ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#setBeanNameGenerator
*/
public void setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator) {
this.reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
this.scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator);
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR, beanNameGenerator);
}
/**
* Set the {@link ScopeMetadataResolver} to use for detected bean classes.
* <p>
* The default is an {@link AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver}.
* <p>
* Any call to this method must occur prior to calls to {@link #register(Class...)}
* and/or {@link #scan(String...)}.
* @param scopeMetadataResolver the scope metadata resolver
*/
public void setScopeMetadataResolver(ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver) {
this.reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
this.scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver);
}
/**
* Register one or more annotated classes to be processed. Note that
* {@link #refresh()} must be called in order for the context to fully process the new
* class.
* <p>
* Calls to {@code #register} are idempotent; adding the same annotated class more
* than once has no additional effect.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes, e.g. {@code @Configuration}
* classes
* @see #scan(String...)
* @see #refresh()
*/
@Override
public final void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.annotatedClasses.addAll(Arrays.asList(annotatedClasses));
}
/**
* Perform a scan within the specified base packages. Note that {@link #refresh()}
* must be called in order for the context to fully process the new class.
* @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes
* @see #register(Class...)
* @see #refresh()
*/
@Override
public final void scan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
this.basePackages = basePackages;
}
@Override
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.scanner.clearCache();
super.prepareRefresh();
}
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
this.reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses));
}
}
}