数据绑定这个概念在任何一个成型的框架中都是特别重要的,它能让框架更多的自动化,更好容错性以及更高的编码效率。它提供的能力是:把字符串形式的参数转换成服务端真正需要的类型的转换(当然还包含校验)。对 Spring 中的数据绑定场景,Controller 中只需要使用 Model 对象就能完成 request 到 Model 对象的自动数据自动绑定,完全屏蔽了 Servlet 的 API。
BeanWrapper
BeanWrapper 是对 Bean 的包装,其接口中所定义的功能有:获取包装对象、设置包装对象的属性值(PropertyAccessor),还可以进行属性类型的转换。
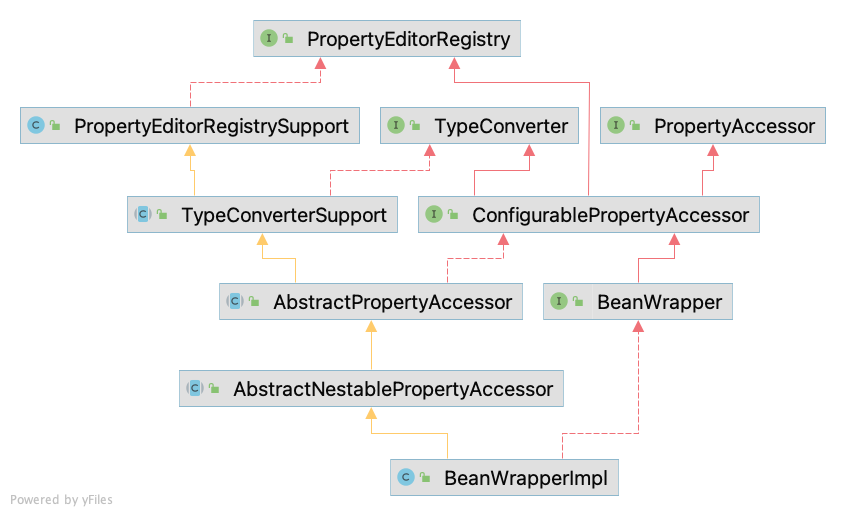
BeanWrapper 用法比较简单,其转换逻辑都依赖于 PropertyEditor 以及 Converter Framework,在获取不到合适的 PropertyEditor 以及 Converter 时,其委托的 TypeConverter 会调用待转换类型的构造函数试图构造出对应的类型,因此会出现以下这样的情况。
@Data
public class Person {
private Date birthday;
private Date end;
private Date endTest;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
BeanWrapper wrapper = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(person);
wrapper.setPropertyValue("birthday", ); // Sat Sep 11 17:22:06 CST 2021
System.out.println(person); // set success
}讲了这么多,接下来讲到的 DataBinder 对于属性的设置全部委托给 BeanWrapper 进行。
DataBinder
类型转换及格式化最终会依托于 PropertyEditor 和 Converter Framework 来实现具体属性值的转换。默认注册逻辑在 PropertyEditorRegistrySupport#createDefaultEditors(),当然我们也可以通过自定义并注册 PropertyEditor 的方式优雅地使用 DataBinder。
Person person = new Person();
DataBinder binder = new DataBinder(person, "person");
binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new DatePropertyEditor());
//binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, "birthday", new MyDatePropertyEditor());
MutablePropertyValues pvs = new MutablePropertyValues();
pvs.add("name", "fsx");
pvs.add("birthday", "2019-07-20");
binder.bind(pvs);
System.out.println(person);WebDataBinder
WebBindingInitializer
WebBindingInitializer:实现此接口重写 initBinder 方法注册的属性编辑器是全局的属性编辑器,对所有的 Controller 都有效。可以理解为:WebBindingInitializer 为编码方式,@InitBinder 为注解方式(注解方式能控制到只对当前 Controller 有效,实现更细粒度的控制)。
public interface WebBindingInitializer {
void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder);
}@InitBinder //只对当前 Controller 有效,配合 @ControllerAdvice 可全局生效
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setDisallowedFields("name");
}此接口它的内建唯一实现类为:ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer,若你自己想要扩展,建议继承它。
public class ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer implements WebBindingInitializer {
private boolean autoGrowNestedPaths = true;
private boolean directFieldAccess = false; // 显然这里是false
@Nullable
private MessageCodesResolver messageCodesResolver;
@Nullable
private BindingErrorProcessor bindingErrorProcessor;
@Nullable
private Validator validator;
@Nullable
private ConversionService conversionService;
// 此处使用的PropertyEditorRegistrar来管理的,最终都会被注册进PropertyEditorRegistry嘛
@Nullable
private PropertyEditorRegistrar[] propertyEditorRegistrars;
... // 省略所有get/set
@Override
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(this.autoGrowNestedPaths);
if (this.directFieldAccess) {
binder.initDirectFieldAccess();
}
if (this.messageCodesResolver != null) {
binder.setMessageCodesResolver(this.messageCodesResolver);
}
if (this.bindingErrorProcessor != null) {
binder.setBindingErrorProcessor(this.bindingErrorProcessor);
}
// 可以看到对校验器这块 内部还是做了容错的
if (this.validator != null && binder.getTarget() != null && this.validator.supports(binder.getTarget().getClass())) {
binder.setValidator(this.validator);
}
if (this.conversionService != null) {
binder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
}
if (this.propertyEditorRegistrars != null) {
for (PropertyEditorRegistrar propertyEditorRegistrar : this.propertyEditorRegistrars) {
propertyEditorRegistrar.registerCustomEditors(binder);
}
}
}
}WebDataBinderFactory Tree
顾名思义它就是来创造一个WebDataBinder的工厂。
public interface WebDataBinderFactory {
WebDataBinder createBinder(NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable Object target, String objectName) throws Exception;
}它的继承树如下:
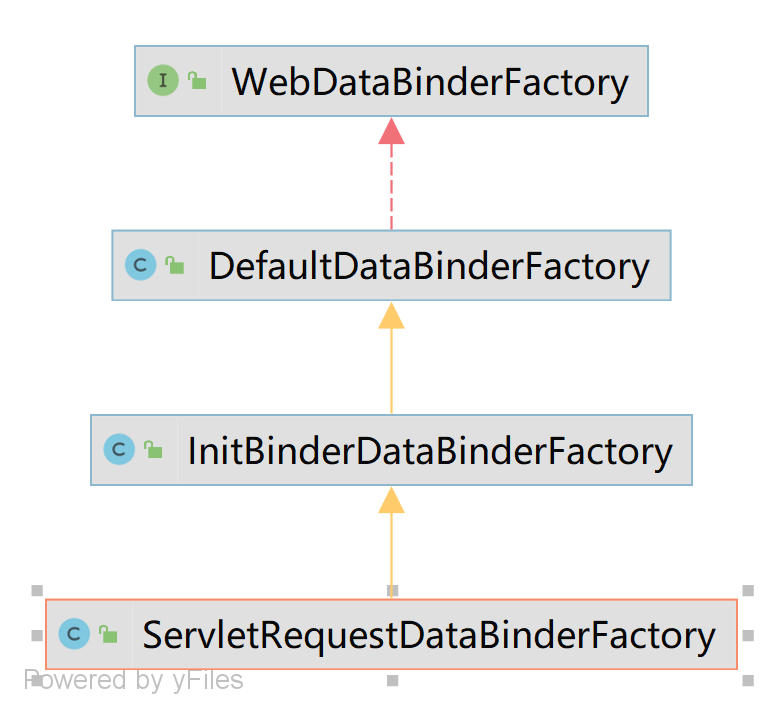
DefaultDataBinderFactory
public class DefaultDataBinderFactory implements WebDataBinderFactory {
@Nullable
private final WebBindingInitializer initializer;
public DefaultDataBinderFactory(@Nullable WebBindingInitializer initializer) {
this.initializer = initializer;
}
// 实现接口的方法
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public final WebDataBinder createBinder(NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable Object target, String objectName) throws Exception {
WebDataBinder dataBinder = createBinderInstance(target, objectName, webRequest);
// 可见WebDataBinder 创建好后,此处就会回调(只有一个)
if (this.initializer != null) {
this.initializer.initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
}
// 空方法 子类去实现,比如InitBinderDataBinderFactory实现了词方法
initBinder(dataBinder, webRequest);
return dataBinder;
}
// 子类可以复写,默认实现是 WebRequestDataBinder
// 比如子类 ServletRequestDataBinderFactory 就复写了,使用的 new ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder(target, objectName)
protected WebDataBinder createBinderInstance(@Nullable Object target, String objectName, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception
return new WebRequestDataBinder(target, objectName);
}
}InitBinderDataBinderFactory
它继承自 DefaultDataBinderFactory,主要用于处理标注有 @InitBinder 的方法做初始绑定。
public class InitBinderDataBinderFactory extends DefaultDataBinderFactory {
// 需要注意的是:@InitBinder 可以标注N多个方法,所以此处是List
private final List<InvocableHandlerMethod> binderMethods;
public InitBinderDataBinderFactory(@Nullable List<InvocableHandlerMethod> binderMethods, @Nullable WebBindingInitializer initializer) {
super(initializer);
this.binderMethods = (binderMethods != null ? binderMethods : Collections.emptyList());
}
// 上面知道此方法的调用方法生initializer.initBinder之后
// 所以使用注解它生效的时机是在直接实现接口的后面的~
@Override
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder, NativeWebRequest request) throws Exception {
for (InvocableHandlerMethod binderMethod : this.binderMethods) {
// 判断@InitBinder是否对dataBinder持有的target对象生效~~~(根据name来匹配的)
if (isBinderMethodApplicable(binderMethod, dataBinder)) {
Object returnValue = binderMethod.invokeForRequest(request, null, dataBinder);
// 标注@InitBinder的方法不能有返回值
if (returnValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@InitBinder methods must not return a value (should be void): " + binderMethod);
}
}
}
}
// @InitBinder 有个 Value 值,它是个数组。它是用来匹配 dataBinder.getObjectName() 是否匹配的
//若匹配上了,现在此注解方法就会生效, 若 value 为空,那就对所有生效。
protected boolean isBinderMethodApplicable(HandlerMethod initBinderMethod, WebDataBinder dataBinder) {
InitBinder ann = initBinderMethod.getMethodAnnotation(InitBinder.class);
Assert.state(ann != null, "No InitBinder annotation");
String[] names = ann.value();
return (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(names) || ObjectUtils.containsElement(names, dataBinder.getObjectName()));
}
}ServletRequestDataBinderFactory
它继承自 InitBinderDataBinderFactory,作用就更明显了。既能够处理 @InitBinder,而且它使用的是更为强大的数据绑定器:ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder
public class ServletRequestDataBinderFactory extends InitBinderDataBinderFactory {
public ServletRequestDataBinderFactory(@Nullable List<InvocableHandlerMethod> binderMethods, @Nullable WebBindingInitializer initializer) {
super(binderMethods, initializer);
}
@Override
protected ServletRequestDataBinder createBinderInstance(
@Nullable Object target, String objectName, NativeWebRequest request) throws Exception {
return new ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder(target, objectName);
}
}此工厂是 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 这个适配器默认使用的一个数据绑定器工厂,而 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 却又是当下使用得最频繁、功能最强大的一个适配器。
WebDataBinder Tree
WebDataBinder
它的作用就是从 Request 把 Web 请求的 parameters 绑定到 JavaBean 上。Controller 方法的参数类型可以是基本类型,也可以是封装后的普通 Java 类型。若这个普通 Java 类型没有声明任何注解,则意味着它的每一个属性都需要到 Request 中去查找对应的请求参数。
public class WebDataBinder extends DataBinder {
// 此字段意思是:字段标记 比如name -> _name
// 这对于HTML复选框和选择选项特别有用。
public static final String DEFAULT_FIELD_MARKER_PREFIX = "_";
// !符号是处理默认值的,提供一个默认值代替空值。
public static final String DEFAULT_FIELD_DEFAULT_PREFIX = "!";
@Nullable
private String fieldMarkerPrefix = DEFAULT_FIELD_MARKER_PREFIX;
@Nullable
private String fieldDefaultPrefix = DEFAULT_FIELD_DEFAULT_PREFIX;
// 默认也会绑定空的文件流
private boolean bindEmptyMultipartFiles = true;
// 在父类的基础上,增加了对_和!的处理
@Override
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkFieldDefaults(mpvs);
checkFieldMarkers(mpvs);
super.doBind(mpvs);
}
// 单独提供的方法,用于绑定 org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile 类型的数据到 JavaBean 属性上
// 显然默认是允许 MultipartFile 作为 Bean 一个属性参与绑定的
// Map<String, List<MultipartFile>> 它的key,一般来说就是文件名
protected void bindMultipart(Map<String, List<MultipartFile>> multipartFiles, MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
multipartFiles.forEach((key, values) -> {
if (values.size() == 1) {
MultipartFile value = values.get(0);
if (isBindEmptyMultipartFiles() || !value.isEmpty()) {
mpvs.add(key, value);
}
}
else {
mpvs.add(key, values);
}
});
}
}单从WebDataBinder来说,它对父类进行了增强,提供的增强能力如下:
- 支持对属性名以
_打头的默认值处理(自动挡,能够自动处理所有的 Bool、Collection、Map 等) - 支持对属性名以
!打头的默认值处理(手动档,需要手动给某个属性赋默认值,自己控制的灵活性很高) - 提供方法,支持把 MultipartFile 绑定到 JavaBean 的属性上
ServletRequestDataBinder
ServletRequestDataBinder 是请求参数绑定对于 Servlet 规范的适配实现。
public class ServletRequestDataBinder extends WebDataBinder {
// 注意:这不是父类的方法,是本类增强的。
// 意思就是 kv 都从 request 里来,当然内部还是适配成了一个 MutablePropertyValues
public void bind(ServletRequest request) {
// 内部最核心方法是它:WebUtils.getParametersStartingWith() 把 request 参数转换成一个 Map
// request.getParameterNames()
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = new ServletRequestParameterPropertyValues(request);
MultipartRequest multipartRequest = WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartRequest.class);
// 调用父类的bindMultipart方法,把MultipartFile都放进MutablePropertyValues里去
if (multipartRequest != null) {
bindMultipart(multipartRequest.getMultiFileMap(), mpvs);
}
// 这个方法是本类留出来的一个扩展点,子类可以复写此方法自己往里继续添加
// ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder 复写此方法、支持 uriTemplateVariables 的绑定
addBindValues(mpvs, request);
doBind(mpvs);
}
// 这个方法和父类的close方法类似,很少直接调用
public void closeNoCatch() throws ServletRequestBindingException {
if (getBindingResult().hasErrors()) {
throw new ServletRequestBindingException("Errors binding onto object '" + getBindingResult().getObjectName() + "'", new BindException(getBindingResult()));
}
}
}ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder
它是对 ServletRequestDataBinder 的一个增强,它用于把 URI template variables 参数添加进来用于绑定。它会去从 request 的 HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables"; 这个属性里查找到值出来用于绑定。
比我们熟悉的 @PathVariable 它就和这相关:它负责把参数从 url 模版中解析出来,然后放在 attr 上,最后交给 ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder 进行绑定。
介于此:我觉得它还有一个作用,就是定制我们全局属性变量用于绑定~
向此属性放置值的地方是:
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.lookupHandler()—>chain.addInterceptor(new UriTemplateVariablesHandlerInterceptor(uriTemplateVariables));—>preHandle()方法->exposeUriTemplateVariables(this.uriTemplateVariables, request);->request.setAttribute(URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, uriTemplateVariables);
public class ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder extends ServletRequestDataBinder {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void addBindValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs, ServletRequest request) {
// 它的值是:HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
String attr = HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE;
// 注意:此处是attr,而不是parameter
Map<String, String> uriVars = (Map<String, String>) request.getAttribute(attr);
if (uriVars != null) {
uriVars.forEach((name, value) -> {
// 若已经存在确切的key了,不会覆盖
if (mpvs.contains(name)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Skipping URI variable '" + name + "' because request contains bind value with same name.");
}
} else {
mpvs.addPropertyValue(name, value);
}
});
}
}
}可见,通过它我们亦可以很方便的做到在每个ServletRequest提供一份共用的模版属性们,供以绑定
MapDataBinder
它位于 org.springframework.data.web 是和 Spring Data 相关,专门用于处理 target 是 Map
它用的属性访问器是
MapPropertyAccessor:一个继承自AbstractPropertyAccessor的私有静态内部类(也支持到了 SpEL 哦)