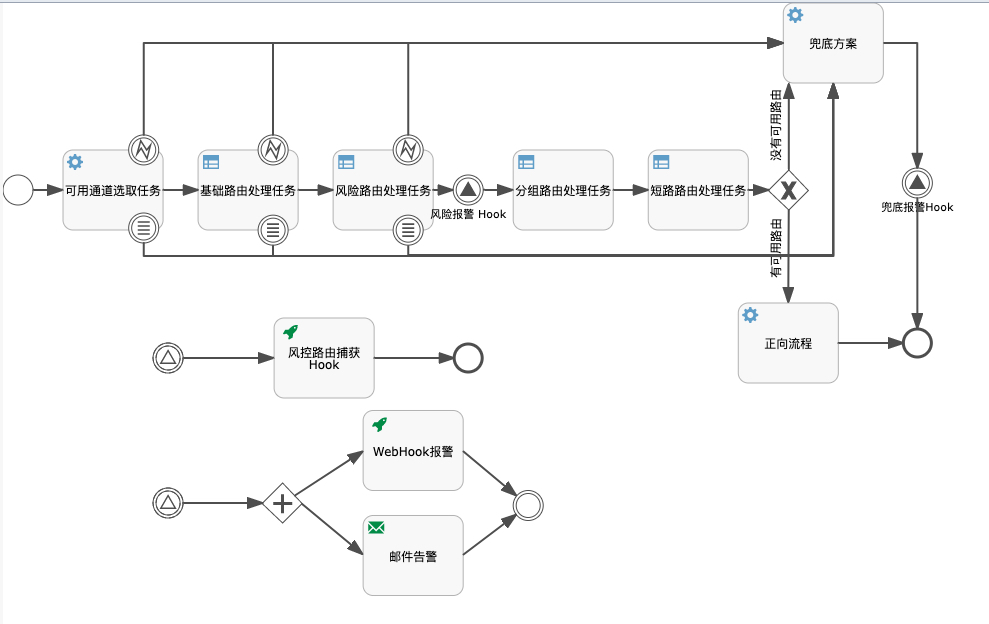
Flowable 实践场景
场景应用
流程变量
在 Flowable 中,变量即在不同的生命周期划分内有效的数据,其主要用于表达式及为 ServiceTask 提供输入及结果存储。
根据生命周期,我们可以将 Flowable 的执行过程划分为:Process、Execution、Task 三种。

对于全局变量来说,它在所有执行过程中都生效;对于局部变量来说,其只在该执行中可见,对执行树的上层则不可见。且局部变量只在相应的执行过程内有效。
我们可在 RuntimeService 和 TaskService 调用关于流程变量的 API(Local API 为局部变量,非 Local API 为流程变量):
setVariable
setVariables
setVariableLocal
setVariablesLocal
hasVariable
hasVariableLocal
getVariable
getVariables
getVariableInstance
getVariableInstances
getVariableLocal
getVariablesLocal
getVariableInstanceLocal
getVariableInstancesLocalByTaskIds
getVariableInstancesLocal
removeVariable
removeVariables
removeVariableLocal
removeVariablesLocal任务审批
在 Flowable 中,审批节点即 UserTask,我们可以通过对其设置多个候选人或者候选人组并从候选人中选择参与者来完成任务。
设置项
flowable:candidateUsers 或 flowable:candidateGroups任务的查询
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionId("processDefinitionId")
.taskCandidateUser("审批人")
.list();任务的拾取
任务被候选人拾取后,其他候选人不可拾取任务。
taskService.claim("taskId", "审批人");任务的归还
如果候选人拾取任务后不想处理,可以归还任务,这样其他候选人又可以拾取这个任务了。
taskService.unclaim("taskId");任务的交接
如果候选人拾取了任务,但是不想执行,那么可以把这个任务交接给其他的用户。
taskService.setAssignee("taskId", "另一个审批人");任务的完成
taskService.complete("taskId");任务回退
我们通过移动对应流程实例对应的 ACT_ID 来实现任务的回退。
串行回退
ProcessEngine processEngine = flowableService.getProcessEngineInstance();
processEngine
.getRuntimeService().createChangeActivityStateBuilder()
.processInstanceId("processInstanceId")
.moveActivityIdTo("currentActivityId", "newActivityId");同理可知
moveActivityIdsToSingleActivityId 并行回退
moveExecutionToActivityId 不关心当前 ACT 节点的回退任务失败重试
在 Flowable 中,节点可以分为开始节点、中间执行节点、中间暂停节点、结束节点,而节点执行方式也可分为同步执行和异步执行。对于同步执行来讲,任务由开始节点或中间暂停节点开始执行,如果成功则到达中间暂停节点或结束节点,如果失败则回滚至该阶段的起点。而异步执行则有所不同,凡是被设置为异步执行的节点都被包装成了异步任务,如果异步节点执行失败则会重试(默认为三次),全部失败后进入死信队列被持久化到 ACT_RU_DEADLETTER_JOB 数据库。
由上面叙述我们可知可以由 ACT_RU_DEADLETTER_JOB 数据库得知目前因失败阻塞的任务。我们还需要通过手动的方式重试失败的任务使其成功,调用 API 如下:
moveJobToDeadLetterJob 将任务移动到死信队列
moveDeadLetterJobToExecutableJob 将死信队列中的任务重试执行为流程实例添加名称
待办任务列表有一列是流程实例的名称(即标题),方便识别每个流程对应的业务含义。
// 获取流程构造器
ProcessInstanceBuilder processInstanceBuilder = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceBuilder();
// 设置参数
processInstanceBuilder.name("王子豪 2022-06-30 退货 110023231231"); // 流程实例标题
processInstanceBuilder.businessKey("BUSINESS_KEY"); // 业务key
processInstanceBuilder.processDefinitionId("aftersale:0001"); //流程定义key
// 启动(即创建)流程实例
ProcessInstance instance = processInstanceBuilder.start();决策表引擎
在流程编排的背景下,大部分业务需要各式各样复杂的判断规则和场景,而这些规则写入代码并不方便做版本管理和热更新,因此应用决策表可将大多数判断校验条件集成在 XML 文件中,帮助完成对应需求,减轻开发量和变更成本。
决策表需要额外的 Maven 依赖才可以使用。
<!--决策引擎dmn-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-dmn-engine-configurator</artifactId>
<version>6.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-dmn-engine</artifactId>
<version>6.3.0</version>
</dependency>项目引用 DMN 引擎
DmnEngineConfiguration dmnEngineConfiguration = DmnEngineConfiguration.createStandaloneDmnEngineConfiguration()
.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/flowable?autoReconnect=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8")
.setJdbcUsername("root")
.setJdbcPassword("123456")
.setJdbcDriver("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver")
// 如果数据表不存在的时候,自动创建数据表
.setDatabaseSchemaUpdate(ProcessEngineConfiguration.DB_SCHEMA_UPDATE_TRUE);
DmnEngine dmnEngine = dmnEngineConfiguration.buildDmnEngine();与 Flowable 一样,其也需要多个 Service 管理其生命周期。
// 获取 RepositoryService
DmnRepositoryService dmnRepositoryService = dmnEngine.getDmnRepositoryService();
// 发布资源
dmnRepositoryService.createDeployment().name("dmnsample.dmn.xml")
.addClasspathResource("dmnsample.dmn.xml")
.deploy();
// 获取 RuleService
DmnRuleService dmnRuleService = dmnEngine.getDmnRuleService();
Map<String, Object> inputVariables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
inputVariables.put("input1", 11);
// 执行规则引擎
List<Map<String, Object>> result = dmnRuleService.executeDecisionByKey("decision", inputVariables);
System.out.println(result);下面附上决策表定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/DMN/20151101" id="simple" name="Simple" namespace="http://flowable.org/dmn">
<decision id="decision" name="Simple decision">
<decisionTable id="decisionTable">
<input>
<inputExpression id="input1" typeRef="number">
<text>input1</text>
</inputExpression>
</input>
<output id="output1" label="Output 1" name="output1" typeRef="string" />
<output id="output2" label="Output 2" name="output2" typeRef="number" />
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry1">
<text><![CDATA[> 10]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry1_1">
<text>'test'</text>
</outputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry2_1">
<text>1</text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry2">
<text><![CDATA[< 10]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry1_2">
<text>'test2'</text>
</outputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry2_2">
<text>2</text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
<rule>
<inputEntry id="inputEntry3">
<text><![CDATA[== 10]]></text>
</inputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry1_3">
<text>'test3'</text>
</outputEntry>
<outputEntry id="outputEntry2_3">
<text>3</text>
</outputEntry>
</rule>
</decisionTable>
</decision>
</definitions>与 Flowable 集成
<serviceTask id="sid-64DC19A4-1CBA-45C6-859F-83F3EE44C7F4" name="决策表" flowable:type="dmn">
<extensionElements>
<flowable:field name="decisionTableReferenceKey">
<flowable:string><![CDATA[decision]]></flowable:string>
</flowable:field>
<flowable:field name="decisionTaskThrowErrorOnNoHits">
<flowable:string><![CDATA[false]]></flowable:string>
</flowable:field>
</extensionElements>
</serviceTask>表单引擎
Flowable 提供了一种简便灵活的方式,用来为业务流程中的人工步骤添加表单。 有两种使用表单的方法:使用(由表单设计器创建的)表单定义的内置表单渲染,以及外部表单渲染。 使用外部表单渲染时,可以使用(自Explorer web应用V5版本支持的)表单参数;也可以使用表单 key 定义,引用外部的、使用自定义代码解析的表单。
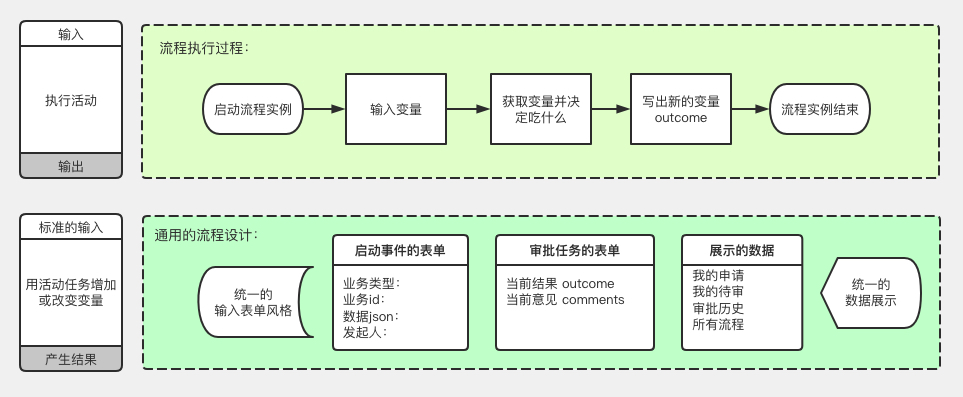
表单引擎会依赖以下六张数据表:
act_fo_databasechangelog: Liquibase用来跟踪数据库变量的
act_fo_databasechangeloglock: Liquibase用来保证同一时刻只有一个Liquibase实例在运行
act_fo_form_definition:存储表单定义的信息
act_fo_form_instance:存储用户填充后表单实例信息
act_fo_form_deployment:存储表单部署元数据
act_fo_form_resource:存储表单定义的资源
内置表单
外置表单
定义表单
表单定义文件是以 .form 为后缀, 内容格式为 Json 格式。如下示例所示。
{
"key": "form1",
"name": "My first form",
"fields": [
{
"id": "input1",
"name": "Input1",
"type": "text",
"required": false,
"placeholder": "empty"
}
],
"outcomes": [
{
"id": "null",
"name": "Accept"
},
{
"id": "null",
"name": "Reject"
}
]
}该文件的 key 属性是其唯一性标识,表单引擎可以通过该 key 获取到它, 同时数据库对相同 key 会维护不同的版本。第二部分是表单字段数组,第三部分是表单结果。每一个表单字段都有 id、name 和 type 属性。id 属性在同一个表单定义文件中必须唯一,当用户赋值时它会作为变量的名称,在上例中,也就是会创建名称为 input1 的变量,值由用户填入。同时表单结果也会以 form_<form-identifier>_outcome 获取得到,对于上例,用户选择的结果会赋值给 form_form1_outcome, 我们可以通过 ${form_form1_outcome == "Accept"} 表达式来验证表单结果是否为 Accept。
部署表单
FormDeployment formDeployment = formRepositoryService.createDeployment()
.addClasspathResource("first.form")
.name("test")
.parentDeploymentId("1")
.deploy();启动任务
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("days","4");
map.put("startTime","20220404");
map.put("reason","出去玩玩");
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceWithForm("processDefinitionId", "outcome", variables, "processInstanceName");项目应用
审批流应用
决策流应用